Ekspertvurdering:
- En eksperts vurdering af hjemmesidens brugervenlighed
- Forholdsvis hurtig test
- Middel ressourcekrævende
- Jakob Nielsens 10 heuristikker:
- Udtryk for brugervenlighed af systemet
- Udviklet af Jakob Nielsen i 90’erne til software-systemer
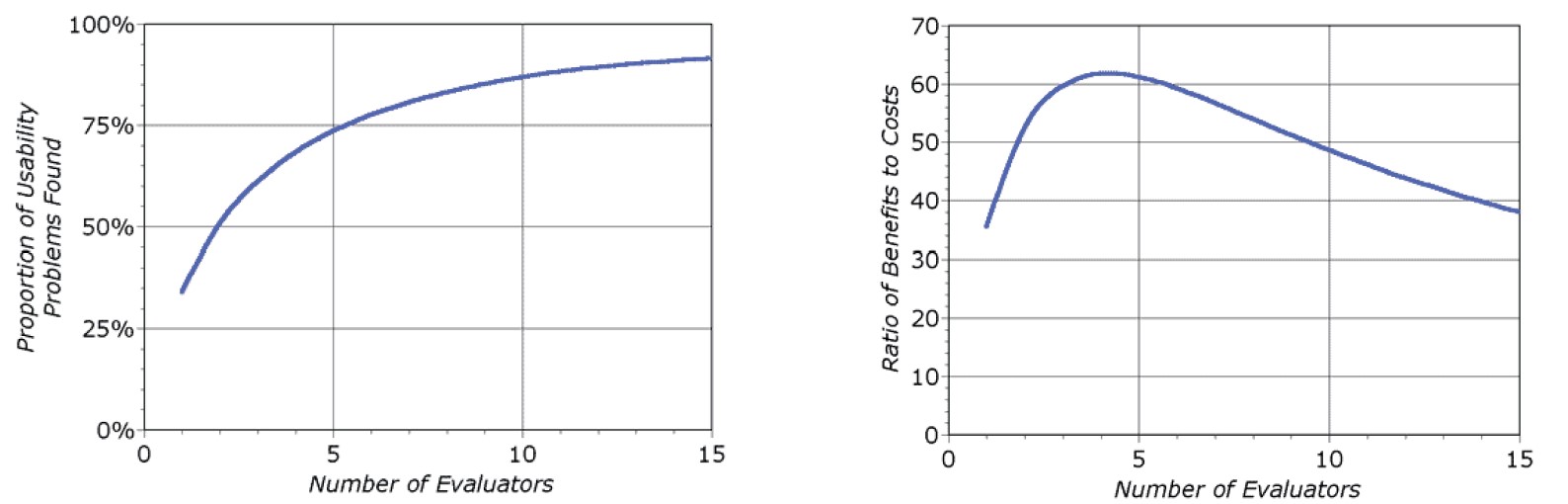
- Middel ressourcer: 4 eksperter - Test af eksisterende hjemmesider / planlægning
Udførelse:
- 4 eksperter vurderer hjemmesiden hver for sig (1 time)
- Tildeler fejl 1-4 point (4 værst)
- Sætter sig sammen og foretager en samlet vurdering
Ekspertvurdering (Jakob Nielsens 10 heuristikker):
- Visibility of system status
The system should always keep users informed about what is going on,
through appropriate feedback within reasonable time. - Match between system and the real world
The system should speak the users' language, with words, phrases and
concepts familiar to the user, rather than system-oriented terms. Follow realworld
conventions, making information appear in a natural and logical order. - User control and freedom
Users often choose system functions by mistake and will need a clearly
marked "emergency exit" to leave the unwanted state without having to go
through an extended dialogue. Support undo and redo. - Consistency and standards
Users should not have to wonder whether different words, situations, or
actions mean the same thing. Follow platform conventions. - Error prevention
Even better than good error messages is a careful design which prevents a
problem from occurring in the first place. Either eliminate error-prone
conditions or check for them and present users with a confirmation option
before they commit to the action. - Recognition rather than recall
Minimize the user's memory load by making objects, actions, and options
visible. The user should not have to remember information from one part
of the dialogue to another. Instructions for use of the system should be
visible or easily retrievable whenever appropriate. - Flexibility and efficiency of use
Accelerators -- unseen by the novice user -- may often speed up the interaction
for the expert user such that the system can cater to both inexperienced and
experienced users. Allow users to tailor frequent actions. - Aesthetic and minimalist design
Dialogues should not contain information which is irrelevant or rarely needed.
Every extra unit of information in a dialogue competes with the relevant units
of information and diminishes their relative visibility. - Help users recognize, diagnose & recover from errors
Error messages should be expressed in plain language (no codes),
precisely indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution.
10.Help and documentation
Even though it is better if the system can be used without documentation,
it may be necessary to provide help and documentation. Any such information
should be easy to search, focused on the user's task, list concrete steps to be
carried out, and not be too large.
Ekspertvurdering:
Ekspertvurdering:
Problemkategorier (kan anvendes til flere tests):
1: Kosmetisk fejl
Fejl eller mangel, som kun har kosmetisk betydning
2: Mindre fejl
Fejl eller mangel, som i begrænset omfang kan have effekt på funktion,
men som ikke påvirker operation eller er årsag til problemer i drift.
3: Alvorlig fejl
Fejl eller mangel, som har alvorlig effekt på operation eller funktion,
men ikke blokerer for gennemførelse af operation.
4: Katastrofal fejl
Fejl eller mangel som bevirker, at en funktion er defekt
eller en operation ikke kan gennemføres.
Kilde:
Det følgende er lånt fra: http://www.useit.com/papers/heuristic/heuristic_list.html
http://www.useit.com/papers/heuristic/heuristic_evaluation.html
Debbie Stone et al. (2005): User Interface Design and Evaluation (cap. 26), Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, USA